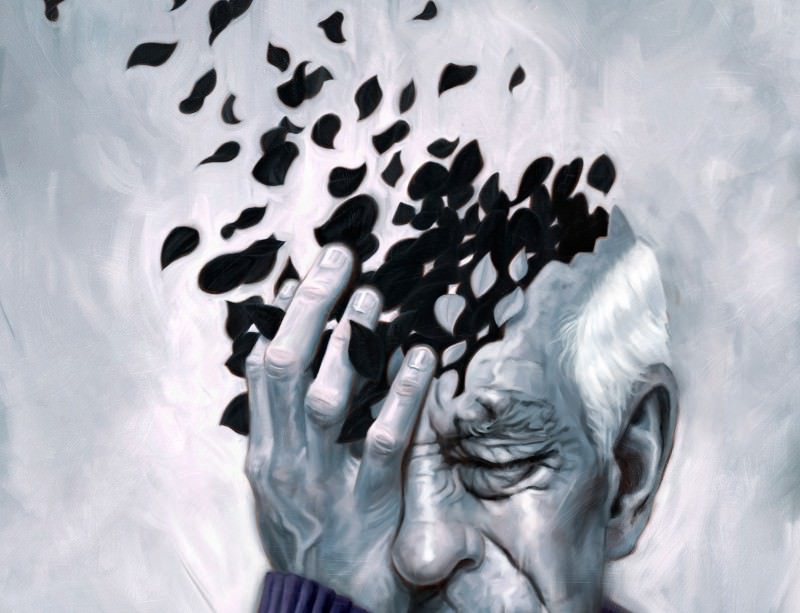
People Living Near To Main Roadways Are More Prone To Dementia: Study Cautions
Are you living close to a highway or busy road? If yes, then the possibilities of your body attracting the risks of Dementia is higher, a newly conducted study warns. The study published on Wednesday, 4th January 2017 has revealed that people living within 200 meters of busy roads or major highway are linked with the bigger risk of dementia.
According to the research paper, around 10% of dementia cases are found among the people living 50m surrounded by a major road. The researchers, in order to conduct the study and conclude precise statistics followed nearly 2 million people in Canada for more than 11 years, and found air pollution and noisy traffic to be the principal reason for the intellectual decline of a person. As suggested by the study, people living areas with higher air pollution and noisy locations are more prone to dementia. The reports of the research have been sent to the dementia experts in the UK for further investigation.
Researchers, during the study, found that currently there are around 50 million people who are suffering from dementia. The individuals residing within 164 feet or 50 meters of a busy road have 7% higher risk of developing dementia, while people living 50 to 100 meters (328 feet) have 4% higher risks of suffering from the same disease. Moreover, the study also suggested lower risks of dementia among the people living 101 to 200 meters (656 feet, or around a 10th of a mile) which stand at 2% only.
While monitoring around two million people living in the Canadian region of Ontario, the analysts found 243,611 diagnosed dementia cases between 2001 and 2012. In comparison to the people living around 300 meters away from the busy roads and noisy locations, people living 50-200 meter areas are more affected by the disease of dementia, the research paper published on Wednesday suggested.
To recall, Dementia is a type of diseases which affect the manner through which people think and intermingle with each other. The disease is mostly associated with the risks of brain damage including the symptoms like short-term memory, hampering intellectuality, affected speech, and motor skills etc.