NASA’s Curiosity detects ‘Rock-Ingredient Stew’ on Mars, Suggests possibility of Life
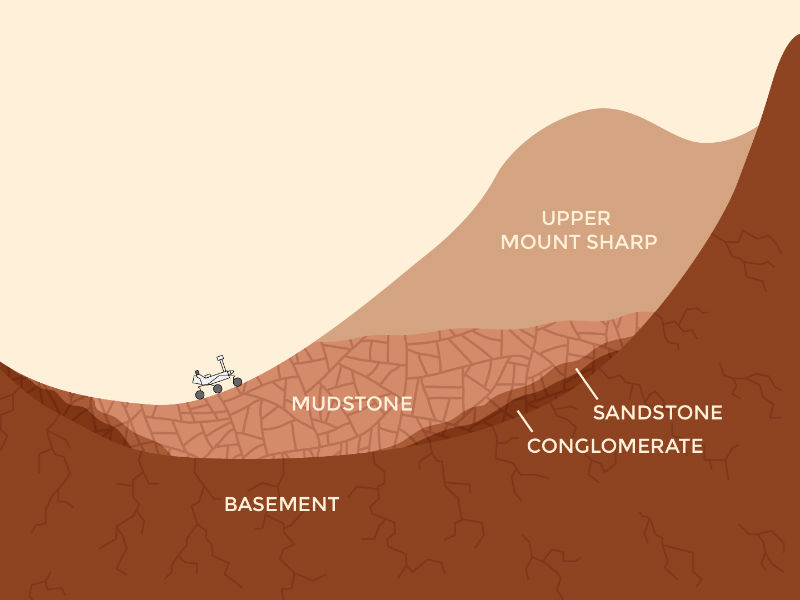
NASA’s Curiosity Rover which is intended to explore Mars and its atmosphere recently found ‘Rock-Ingredient Stew’ on the Martian surface which has triggered the possibility of Life on barren Mars. The robotic rover Curiosity has been exploring Gale Crater on Mars since 2011 with the aim to find some clues about the existence of life on Martian surface. Recently, the rover has detected many rock layers on the planet.
According to the reports of ‘The Space Reporter,’ since 2011 Curiosity Rover has been searching for the higher and younger rocks on the Mars. Throughout the survey; the astronomers have found that the Red Planet contains not only multiple rock layers but also multifaceted water surroundings. While surfing the Gale on the Mars, Curiosity discovered the water bodies to form the sediments, which are intermingling with chemicals because of the groundwater. This evolution now helped the rover to spot the “rock-ingredient stew” that is likely to protract life on the conventional infertile Mars.
As said by John Grotzinger, a crew of Curiosity’s science team and Caltech, the inconsistency on different altitudes of the Red Planet are multiple. Though we now have some solid evidence about the presence of water on the Martian surface, but no official evidence for the existence of life has yet been sourced. And to bring some official confirmation, Curiosity Rover is still on its move to detect the possibilities of microorganism life on Mars.
Though the astronomers haven’t yet confirmed if Mars has life or not, the discovery of rocks is triggering the signs of habitability, which can later be confirmed.
The researchers also have explored the existence of minerals like hematite and elements like boron. According to Grotzinger, the alterations in these minerals and elements point towards the creation of a dynamic system. The minerals by interacting with both the groundwater and surface water can influence the chemistry of the clays. He further explained that a more complicated chemistry creates better possibilities for habitability and Mars has such a complex chemistry of water, mineral, element, and clays.
To summon up, Curiosity is car-sized automatic rover which is developed and operated by NASA. The rover was launched on 26th November, 2011, from Cape Canaveral and landed on the Martian surface on 6th August 2012. The goals behind the Curiosity Rover is exploring the configuration of the climate and geology of Mars, the possibility of microbial life on the Gale Crater of the planet, the investigation of water, and other planetary habitability exploration programs.
Since its landing on Mars, Curiosity has marked many milestones including the discovery of water bodies and the existence of rocks which is showing the possibility of microbial life on Mars.


