Farthest known 500-Million-Year-Old primitive star cluster spotted by NASA
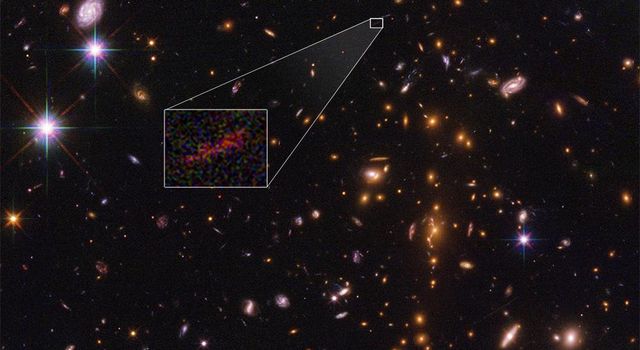
In an image captured via NASA’s Spitzer as well as Hubble Space Telescope, the scientists have discovered a primitive galaxy termed as SPT0615-JD. It is the farthest galaxy known to mankind in the universe. The galaxy is a cluster of primitive stars that came into existence about 500 million years ago. The image of this galaxy is amplified and stretched by the phenomenon termed as gravitational lensing.
Although numerous other galaxies have been found in this periphery of space, they mostly seemed like red dots due to the huge distance gap and small size. This particular galaxy reflected amplified light due to a massive gravitational field from the cluster that increased the visibility of the galaxy while smearing it into an image similar to that of an arc.
The arc-like image of the primitive galaxy provides great insights into the basics of this world far away while no other galaxy at such far distance could be seen clearly to gather enough information, explained Brett Salmon from the Space Telescope Science Institute, the U.S. An analysis of gravitational lensing and its effects on the image obtained of the galaxy can help determine the relevant shape and size of the same.
This theory of warping was first predicted by renowned physicist Albert Einstein, who stated that the gravity from huge objects in the foreground can help brighten as well as distort the image procured of objects in father distance in the background.
This effect is known as “zoom lens” which was used to look for galaxies present in great distances which are hardly ever visible with the modern telescopes available today. This particular galaxy was found when the scientists from NASA used Hubble’s Reionization Lensing Cluster Survey in association with S-RELICS Spitzer program.
The Principal Investigator of RELICS, Dan Coe, stated that the RELICS were constructed to find galaxies located in far away distances that have been brightly magnified to be studied in detail. From the data collected via Spitzer as well as Hubble telescope, the scientists calculated the galaxy’s look back time to be around 13.3 billion years.
An initial analysis of the galaxy suggests that it might be somewhere around 3 billion solar masses in weight. It serves as a great prototype for young galaxies which are less than 2,500 light-years across that were created in a short time frame just after the Big Bang occurred.
This particular galaxy is located just within the limit of the Hubble telescope’s detection capability. However, it is just the beginning phase for the James Webb Space Telescope that is in process of being constructed to be one of the most powerful telescopes yet. With the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, the vast expanse of space gets one inch closer while providing great opportunities for studying the stellar population.


