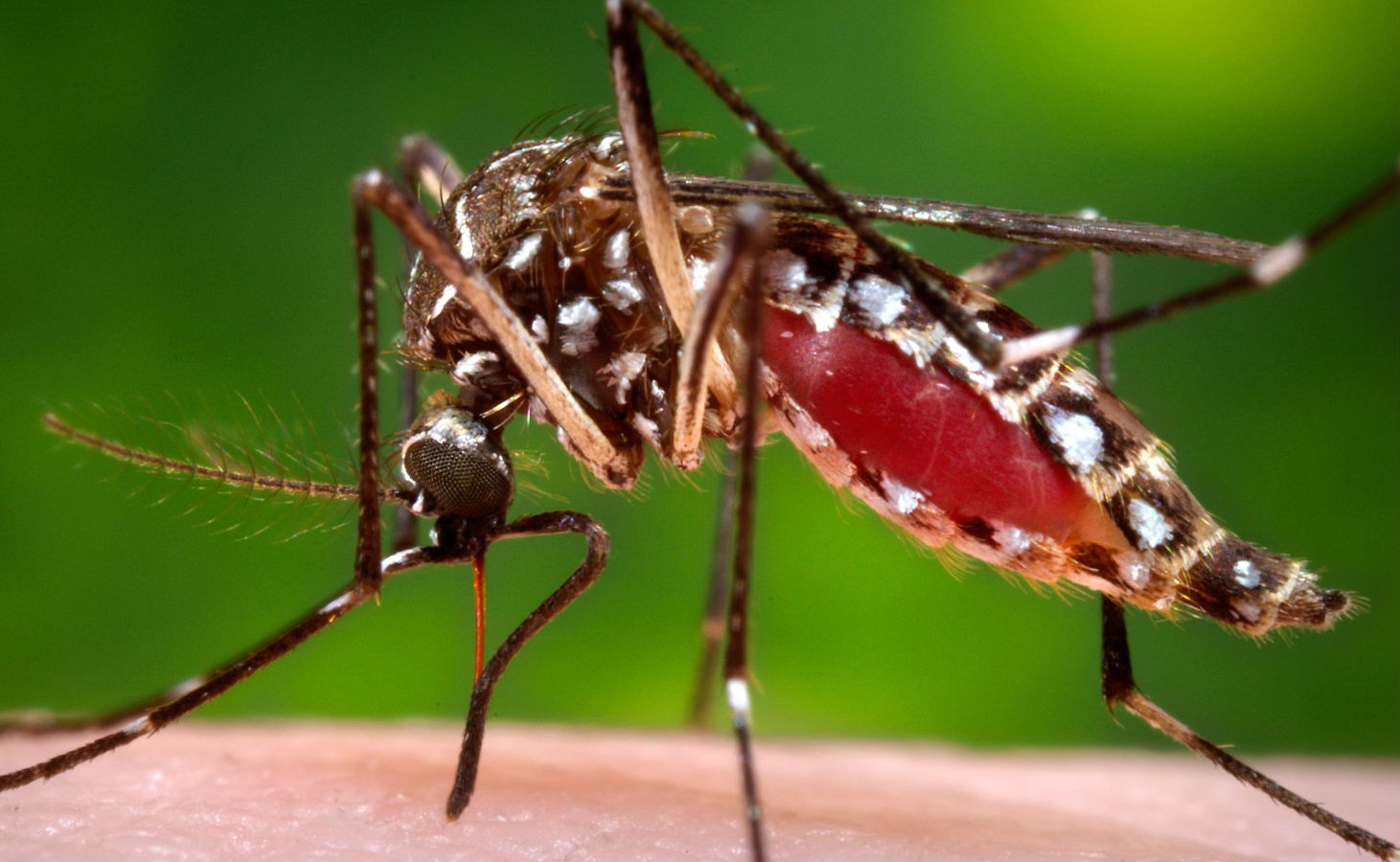
WHO reinforces rules for preventing sexual conduction of Zika virus
Zika Virus, which previously was believed to be a mosquito-borne infirmity, later found to also be dominated by the sexual intercourse practices and to prevent the spread of this disease, World Health Organization (WHO) has strengthened its guidelines. Earlier, Zika Virus is thought to be the principal transmitter of germ to human. The virus was identified as the basic cause behind the formation of catastrophic congenital microcephaly in newborn babies and pregnant women bitten by contaminated mosquitoes. But later, the study conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmed that ZIKV can also be transmitted through sexual intercourse and WHO also verified that, the virus could be transferred between sexual partners.
Now, after finding the sexual transmission to playing a pivotal role in the swell of the Zika Virus, World Health organization has strengthened its guidelines for preventing the disease. The virus transmitted through sexual contacts can be shifted to the newborn babies during the period of pregnancy, WHO confirmed. And to put an end to all these possibilities, WHO has released a new guideline for the sexual contact among people living in Zika-affected locations.
The WHO, in its new rule book for Sexual transmission of Zika, has advised sex partners and couples to use proper contraception while having sex. Moreover, it also suggested staying away from intercourse practice for some period of time. In the new guideline, the WHO requested the couples to stay away from sexual contact for as a minimum of eight weeks after visiting any Zika-affected location.
The new rules have doubled up the existing guidelines for Zika which suggested couples excuse themselves from sex for at least four weeks. The WHO also has advised the men who are suffering from the symptoms of the Zika virus, to abstain from sexual activities or use proper contraception at least for six months. Similarly, for women having the symptoms of the Zika are recommended to remain away from sexual intercourse at least for eight weeks. In addition, the couples who have Zika Virus are advised to wait at least for six months. The symptoms of Zika virus include fever, pain in the back of the eyes, joints, and muscles, loss of appetite, sweating, eye redness, headache, skin rash, or vomiting.